Technical Abstract
TTI Anisotropic PSDM in a Permafrost Region - A Case Study of Point Thomson, North Slope, Alaska
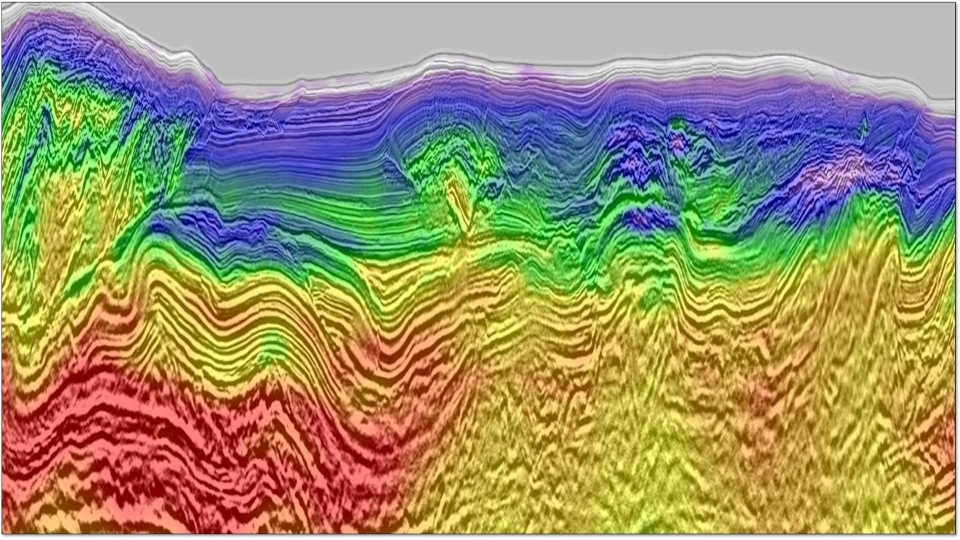
Back to Technical ContentThe Point Thomson field, located on the North Slope of Alaska, covers the transition zone from onshore to a frozen lagoon. This complexity in the near-surface poses many challenges to proper imaging of the reservoir. Unground ice on the lagoon causes very poor signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) over a critical portion of the field. The rapid lateral variation in permafrost thickness introduces strong lateral velocity gradients in the near-surface. Onshore, the presence of ice lakes create highly localized anomalies. We present a workflow that we used to address these near-surface issues during the recent reprocessing of the vintage low-fold data. Aided by modern imaging technology for noise attenuation, statics, and velocity model building, we were able to address many of these issues and produce a significantly improved image.
Download Resource 
Publications
EAGE - European Association of Geoscientists and EngineersAuthors
Liuling Gong, Adam Searle, Chu-Ong Ting, J. Hefti, E. Neumann, J. P. Taylor, M.R. Sarif